West Nile Virus as a model for exotic pathogens transmitted by endemic vectors
Disease description

West Nile virus (WNV) infection is a mosquito-borne zoonosis that is now endemo-epidemic in several countries in Europe. WNV incidence is increasing in the continent and its presence is expanding into new areas where it had never been observed before, becoming a global public health concern. The virus is transmitted among host birds mainly via the bite of infected mosquitoes and incidentally, humans and other mammals may become infected. A number of abiotic (environmental) and biotic factors are known to determine its transmission dynamics.
Temperature is one of the important environmental drivers influencing WNV transmission as it affects either mosquito biology and the extrinsic incubation of the virus.
In face of climatic change, anomalous spring temperatures are considered among the factors affecting the incidence rate and the emergence of the virus into new areas, often associated with new cases in Europe.
Following the analysis of the needs expressed by Public Health and Veterinary Health practitioners, MOOD has dedicated one case study to WNV.
Literature Review
West Nile virus is one of the most widespread flaviviruses worldwide, with high and increasing impact in Europe and Mediterranean countries. Numerous factors should be considered to understand its dynamics, including mosquito vector, avian reservoir and environmental factors which determine its ecology and thus West Nile virus transmission and disease distribution. To better understand which drivers and how they interfere with West Nile epidemiology, a systematic review was conducted.
Disease profile
To reach a comprehensive understanding of the factors affecting the ecology, distribution, and trend in Europe of the infectious diseases included in MOOD, information from the available literature and expert input was collected and summarized in “disease profiles”. These documents synthesize the available knowledge on specific diseases, such as WNV (In Press).
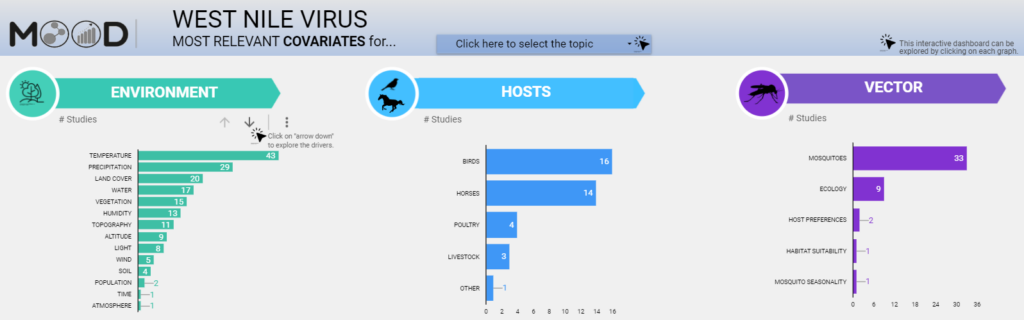
WNV Covariates Dashboard
Fig 5: A snippet of the dashboard for the exploration of WNV covariates.
This tool allows the exploration of metadata about environmental and ecological covariates adopted in literature, with respect to West Nile Virus. The dashboard is based on the results of a literature review performed on articles published between 2000 and 2020.
Publications
- Mencattelli et al. Epidemiological and Evolutionary Analysis of West Nile Virus Lineage 2 in Italy. Viruses. 2023 Jan;15(1):35
- Mencattelli et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of West Nile virus between Africa and Europe. Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 13;14(1):6440
- Fesce et al. Understanding West Nile virus transmission: Mathematical modelling to quantify the most critical parameters to predict infection dynamics. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2023 May 1;17(5):e0010252
- Mencattelli et al. Epidemiology of West Nile virus in Africa: An underestimated threat. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2022 Jan 10;16(1):e0010075.
- Marini et al. Modelling the West Nile virus force of infection in the European human population. One Health. 2022 Dec 1;15:100462.
- Marini et al. Spring temperature shapes West Nile virus transmission in Europe. Acta Tropica. 2021 Mar 1;215:105796.
- Marini et al. Drivers and epidemiological patterns of West Nile virus in Serbia. Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 17;12.
- Giesen et al. A systematic review of environmental factors related to WNV circulation in European and Mediterranean countries. One Health. 2023 June
- Erazo, D., Grant, L., Ghisbain, G. et al. Contribution of climate change to the spatial expansion of West Nile virus in Europe. Nat Commun 15, 1196 (2024).
- Erazo, D., Grant, L., Ghisbain, G. et al. Contribution of climate change to the spatial expansion of West Nile virus in Europe. Nat Commun 15, 1196 (2024).
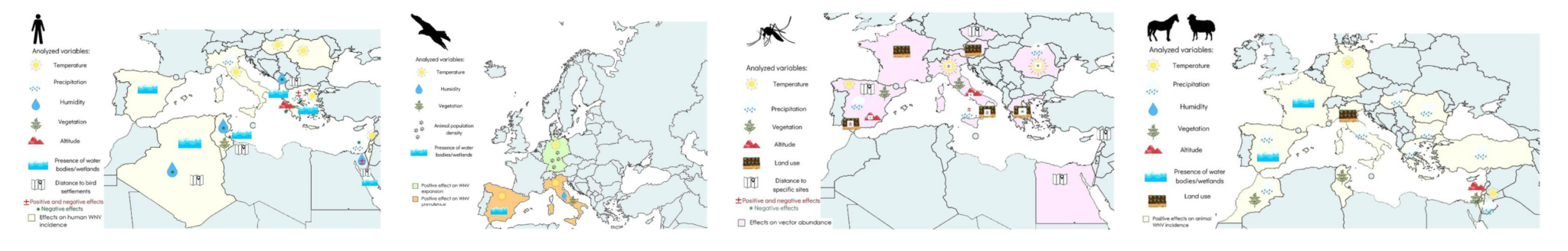
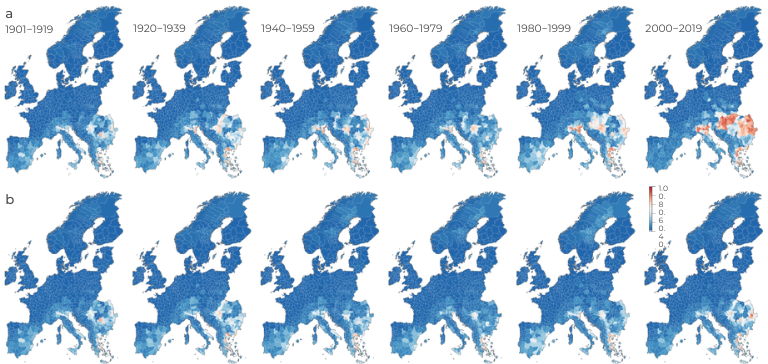
Risk maps
Risk maps were presented for four observationally-based reanalysis climate datasets and their counterfactuals. The counterfactuals approximate a “no climate change” climate through the removal of the long-term trend related to global mean temperature change from the observationally-based datasets. This study was done to study the contribution of climate change (observed long-term trend in climate) to WNV spatial expansion in Europe.
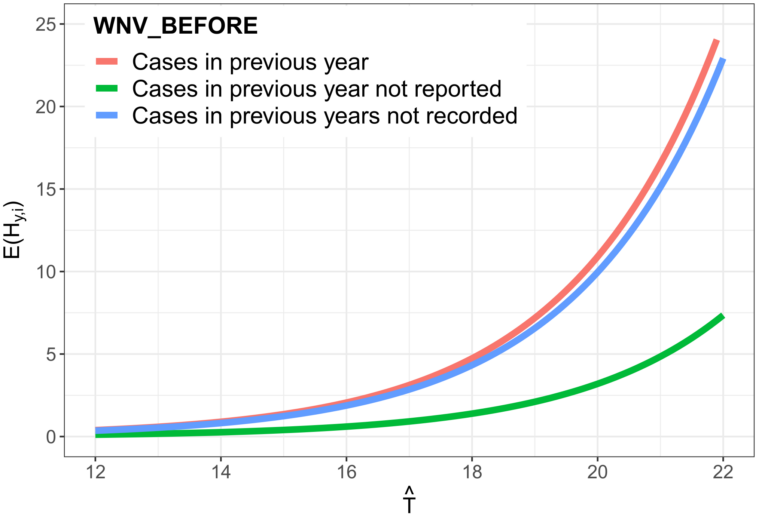
Fig 7: Effect of spring temperature on WNV circulation in Europe
Previous studies have suggested that spring temperature might play a key role at shaping WNV transmission. We tested this hypothesis by carrying out a statistical analysis at European level and found that WNV circulation is higher in usually warmer regions, while warmer than usual springs are associated with a larger number of recorded cases. Hence, we confirmed that weather anomalies at the beginning of the mosquito breeding season might act as an early warning signal for public health authorities, enabling them to strengthen in advance ongoing surveillance and prevention strategies.
Case study leaders




Fondazione Edmund Mach, Research and Innovation Centre, Francesca Dagostin (francesca.dagostin@fmach.it)
Finnish Institute of Health and Welfare, Timothée Dub
Fondazione Edmund Mach, Research and Innovation Centre, Giovanni Marini (giovanni.marini@fmach.it)
Fondazione Mach, Research and Innovation Centre, Annapaola Rizzoli (annapaola.rizzoli@fmach.it)
For more video content about West Nile Virus
Mattia Manicai is a researcher at Fondazione Edmund Mach. His presentation will be centered around one of the most recent publications he has contributed to, titled “Spring temperature shapes West Nile Virus (WNV) transmission in Europe” (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105796). Mattia explains how spatio-temporal conditions will shape WNV transmissions, why WNV circulation tends to be higher in warmer regions, how the impact of change of temperatures due to approaching spring time on WNV transmissions can be predicted, and why new results in conjunction with previous findings can serve as indicators for the reliability of surveillance systems and WNV’s overwintering capacity.
Dr. Laura Kramer has 50 years’ experience studying arboviruses in the field and laboratory, from both experimental and observational approaches, using both classical and molecular tools. She was Director of the Arbovirus Laboratory, Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health from 2000 – Dec 2020 when she retired, and Professor of Biomedical Sciences, State University of New York (SUNY) School of Public Health, Albany, NY. She is also an Adjunct Professor in the Biology department at SUNY Albany. Dr. Kramer also is a virology moderator of ProMED-mail [Program for Monitoring Emerging Diseases] where she reports on COVID-19 and Ebola as well as vaccine-preventable diseases. In this MOOD Science Webinar, Laura discussed her comprehensive research paper “Introduction, Spread, and Establishment of West Nile Virus in the Americas” published on the Journal of Medical Entomology, illustrating the complex relationships among West Nile Virus (WNV), vector mosquitoes and vertebrate hosts, as well as how certain environmental variables – including land use and climate – affected the spillover risk to humans in the United States since its introduction.
Serafin Gutierrez’s main interests are virus ecology and evolution. Along mhis career, he has worked with different viral pathogens of insects, plants and vertebrates. Currently, his group works on various aspects of the ecology and evolution of arthropod-borne viruses, including the discovery of new zoonotic viruses. Moreover, his team explores the viral community or virome of insect vectors and its potential influence on arbovirus epidemiology. In this webinar, Serafin presented a collaborative work on West Nile virus (WNV) and Usutu virus (USUV), including teams involved in both human and veterinary health. These viruses follow a similar enzootic cycle involving mosquitoes and birds. However, they can also infect humans and other mammals, leading to severe disease. Their epidemiological situation may have shifted from irregular epidemics to endemicity in several European regions. This potential change requires confirmation, as it could have implications for risk assessment and surveillance strategies. To this end, the team has evaluated the prevalence and genetics of WNV and USUV in a cross-sectional study in humans, dogs, horses, birds and mosquitoes in the French Camargue area, between 2016 and 2020. Their findings support endemisation in the study region. Serafin also presented future research directions in his group.